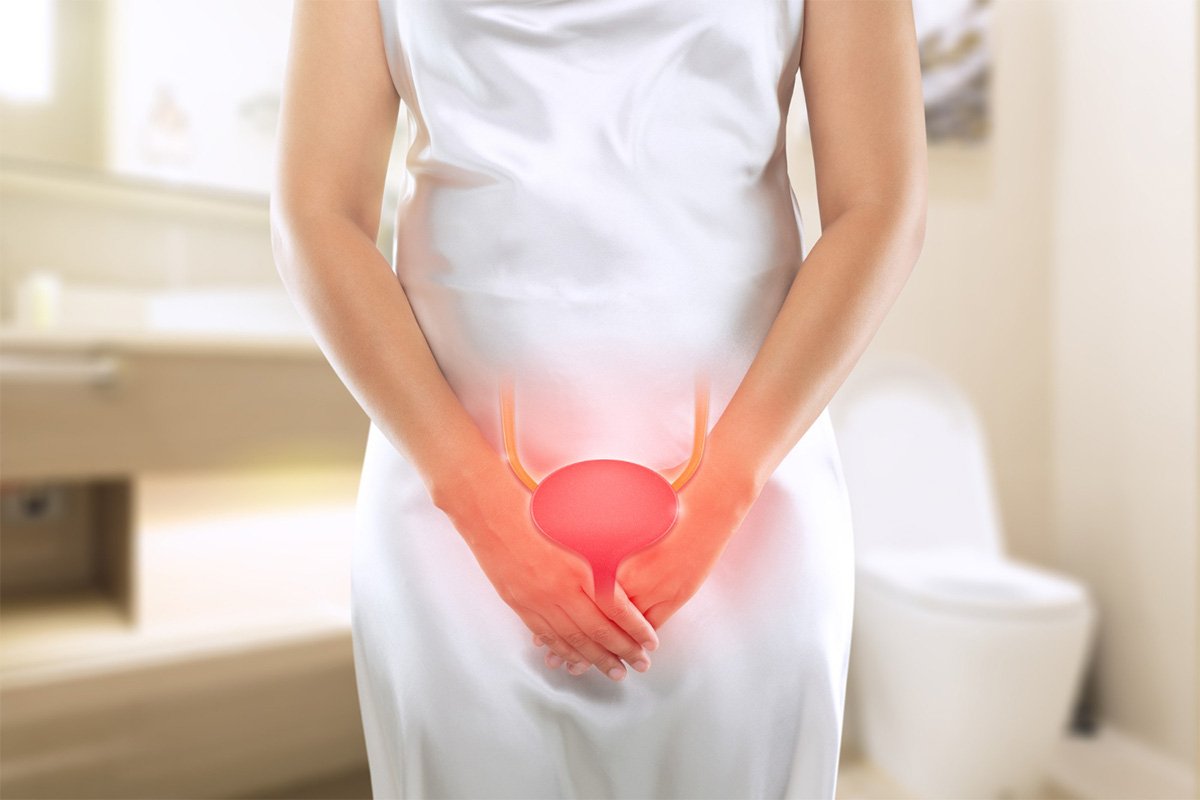
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by an urgent need to urinate, frequent urination, and, in some cases, incontinence, OAB can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Despite its prevalence, many people are hesitant to discuss their symptoms due to embarrassment or lack of awareness. Fortunately, modern medicine offers a range of solutions to manage and treat OAB effectively. This blog will explore these solutions, helping you understand how to regain control and improve your quality of life.
Understanding Overactive Bladder
Before diving into modern treatments, it’s essential to understand what OAB is and what causes it. Overactive bladder occurs when the muscles of the bladder contract involuntarily, even when the bladder isn’t full. This involuntary contraction creates a sudden, urgent need to urinate.
Common Symptoms
- Urgency: A sudden, strong urge to urinate that’s difficult to control.
- Frequency: Needing to urinate more than eight times in 24 hours.
- Nocturia: Waking up more than once at night to urinate.
- Incontinence: Involuntary loss of urine immediately following an urgent need to urinate.
Causes
The exact cause of OAB is often unknown, but several factors can contribute, including:
- Neurological disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can affect bladder function.
- Hormonal changes: Particularly in women during menopause.
- Medications: Some medications can affect bladder control.
- Obstruction: Issues like bladder stones or tumors.
Modern Solutions for Overactive Bladder
Lifestyle Modifications
For many individuals, lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate OAB symptoms. These include:
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing intake of bladder irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods.
- Fluid Management: Monitoring fluid intake to prevent excessive bladder filling.
- Bladder Training: Scheduling bathroom visits and gradually increasing the time between them to train the bladder.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Also known as Kegel exercises, these strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which support the bladder and help control urination. Regular practice can lead to noticeable improvements in bladder control.
Medications
Several medications are available to treat OAB, including:
- Anticholinergics: These reduce bladder muscle spasms and decrease urgency and frequency.
- Beta-3 Agonists: These relax the bladder muscle, increasing its storage capacity and reducing urgency.
- Topical Estrogen: For postmenopausal women, applying estrogen directly to the vaginal area can improve urinary symptoms.
Medical Devices
For those who do not respond to conservative treatments, medical devices offer an alternative solution:
- Bladder Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections: Botox can be injected into the bladder muscle to reduce spasms and improve symptoms.
- Nerve Stimulation: Techniques like sacral neuromodulation or percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation involve stimulating the nerves that control the bladder to improve function.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgical options are available. These are typically considered when other treatments have failed:
- Augmentation Cystoplasty: A procedure to increase bladder capacity by adding a piece of bowel to the bladder.
- Urinary Diversion: Redirecting urine flow to a different part of the body, such as through a stoma.
Emerging Therapies
Research into new treatments for OAB is ongoing, with promising developments on the horizon:
- Gene Therapy: Experimental treatments aimed at altering gene expression to improve bladder function.
- Regenerative Medicine: Using stem cells to repair or regenerate bladder tissue.
Conclusion
Overactive bladder can be a distressing condition, but it’s important to remember that effective treatments are available. From lifestyle changes and exercises to medications, medical devices, and even surgery, modern medicine offers a range of solutions to manage OAB. If you or someone you know is struggling with symptoms of overactive bladder, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. With the right approach, you can regain control and significantly improve your quality of life.