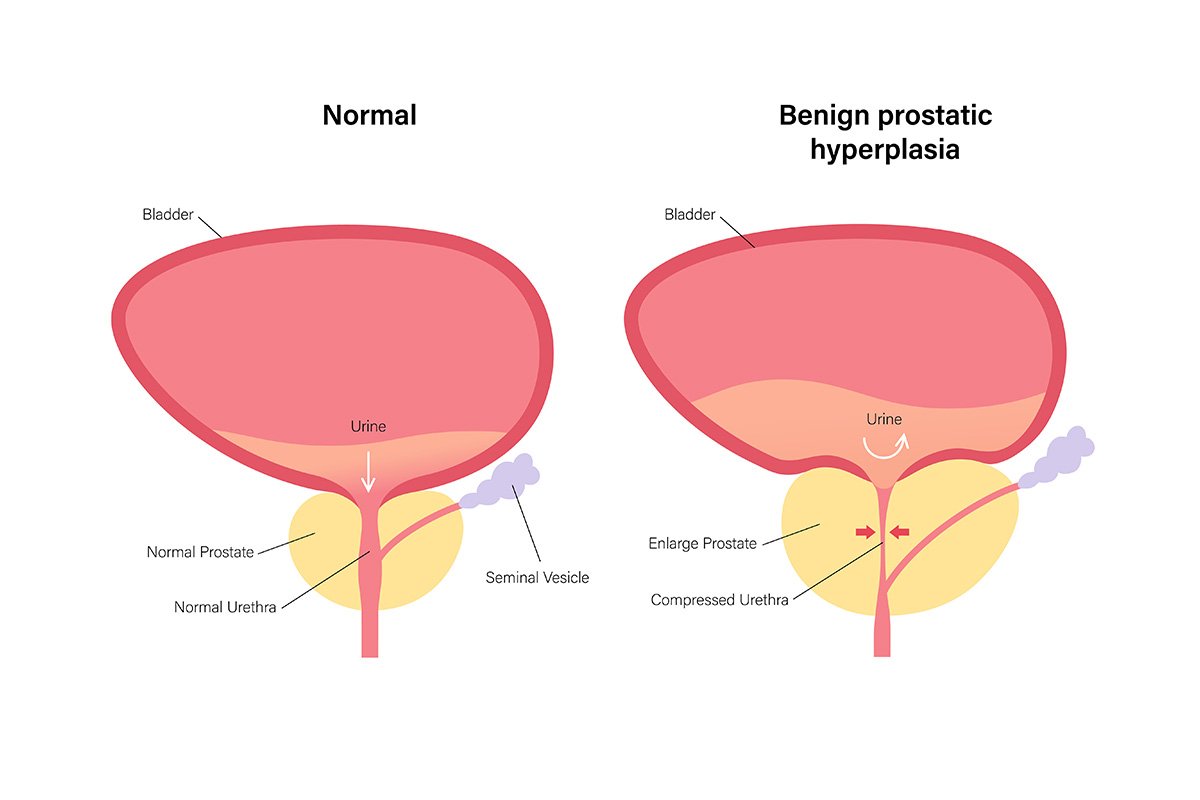
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as an enlarged prostate, is a non-cancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. The prostate is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine passes.
Causes of BPH
- Aging: Hormonal changes related to aging, particularly involving testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a significant role.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of BPH can increase the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, physical activity, and overall health can influence the development of BPH.
Symptoms of BPH
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
- Urgency to urinate
- Dribbling at the end of urination
Complications of BPH
- Acute urinary retention (inability to urinate)
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Bladder stones
- Bladder damage
- Kidney damage
Diagnosis of BPH
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Including a digital rectal exam (DRE).
- Urine Tests: To check for infection or other problems.
- Blood Tests: To check for kidney problems.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: To screen for prostate cancer.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI to visualize the prostate.
- Urodynamic and Pressure Flow Studies: To measure bladder pressure and urine flow.
Treatment of BPH
- Lifestyle Changes
- Reducing fluid intake before bedtime
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
- Regular exercise
- Bladder training techniques
- Medications
- Alpha Blockers: Relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin).
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: Shrink the prostate by blocking hormonal changes (e.g., finasteride, dutasteride).
- Combination Therapy: Using both alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT): Uses microwave energy to destroy prostate tissue.
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA): Uses radiofrequency energy to shrink prostate tissue.
- Surgical Options
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Removal of part of the prostate through the urethra.
- Laser Surgery: Uses lasers to remove prostate tissue.
- Open or Robotic Prostatectomy: Removal of the prostate through an incision.
Proper management of both diabetes and BPH involves regular medical check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to prescribed treatments to improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Services
Need Any Help
Need Any Help, Call Us 24/7 For Support
Call Us
+91 7626017841
Mail Us
drtonykataria@gmail.com
Office Address
